Chart: Area: Excel Area chart example
Example of creating Excel Area charts.
Image of the output file:
Chart 1 in the following example is a default area chart:
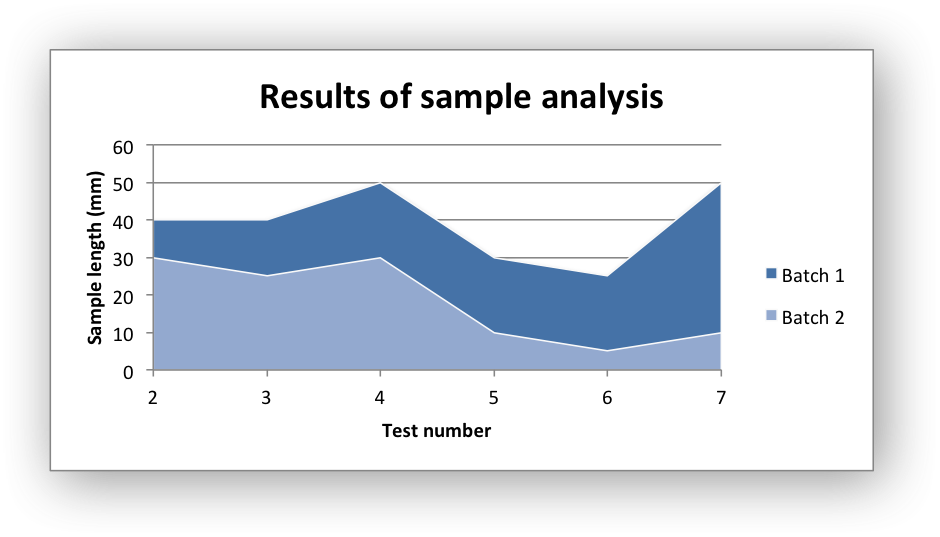
Chart 2 is a stacked area chart:
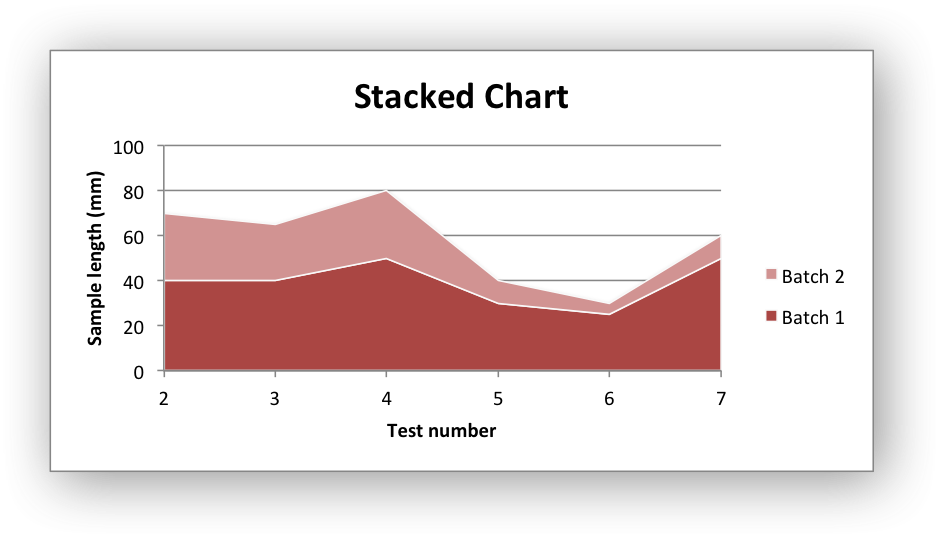
Chart 3 is a percentage stacked area chart:
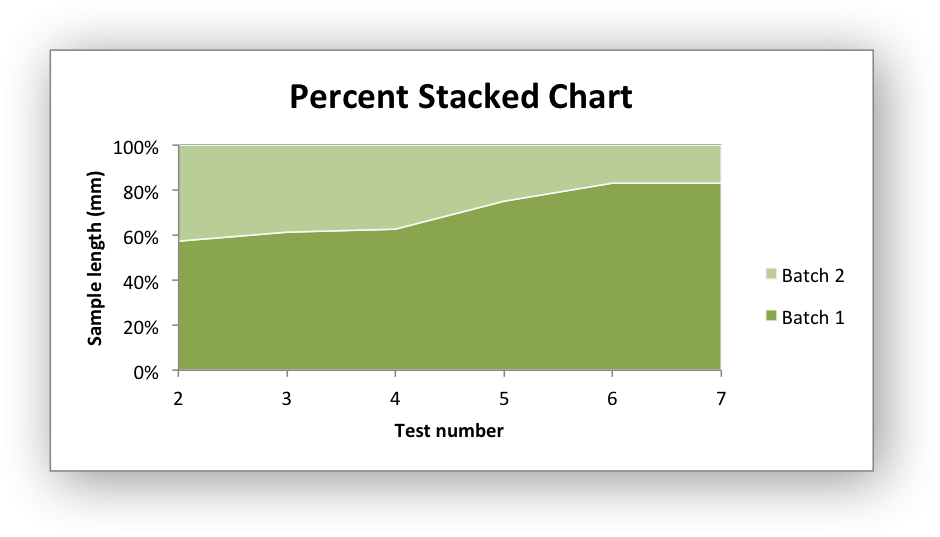
Code to generate the output file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! An example of creating area charts using the `rust_xlsxwriter` library.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Chart, ChartType, Format, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
let bold = Format::new().set_bold();
// Add the worksheet data that the charts will refer to.
worksheet.write_with_format(0, 0, "Number", &bold)?;
worksheet.write_with_format(0, 1, "Batch 1", &bold)?;
worksheet.write_with_format(0, 2, "Batch 2", &bold)?;
let data = [
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[40, 40, 50, 30, 25, 50],
[30, 25, 30, 10, 5, 10],
];
for (col_num, col_data) in data.iter().enumerate() {
for (row_num, row_data) in col_data.iter().enumerate() {
worksheet.write(row_num as u32 + 1, col_num as u16, *row_data)?;
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create a new area chart.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
let mut chart = Chart::new(ChartType::Area);
// Configure the first data series for the chart.
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories("Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7")
.set_values("Sheet1!$B$2:$B$7")
.set_name("Sheet1!$B$1");
// Add another data series to the chart using the alternative tuple syntax
// to describe the range. This method is better when you need to create the
// ranges programmatically to match the data range in the worksheet.
let row_min = 1;
let row_max = data[0].len() as u32;
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories(("Sheet1", row_min, 0, row_max, 0))
.set_values(("Sheet1", row_min, 2, row_max, 2))
.set_name(("Sheet1", 0, 2));
// Add a chart title and some axis labels.
chart.title().set_name("Results of sample analysis");
chart.x_axis().set_name("Test number");
chart.y_axis().set_name("Sample length (mm)");
// Set an Excel chart style.
chart.set_style(11);
// Add the chart to the worksheet.
worksheet.insert_chart_with_offset(1, 3, &chart, 25, 10)?;
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create a stacked chart sub-type.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
let mut chart = Chart::new(ChartType::AreaStacked);
// Configure the first series.
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories("Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7")
.set_values("Sheet1!$B$2:$B$7")
.set_name("Sheet1!$B$1");
// Configure the second series.
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories("Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7")
.set_values("Sheet1!$C$2:$C$7")
.set_name("Sheet1!$C$1");
// Add a chart title and some axis labels.
chart.title().set_name("Stacked Chart");
chart.x_axis().set_name("Test number");
chart.y_axis().set_name("Sample length (mm)");
// Set an Excel chart style.
chart.set_style(12);
// Add the chart to the worksheet.
worksheet.insert_chart_with_offset(17, 3, &chart, 25, 10)?;
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create a percentage stacked chart sub-type.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
let mut chart = Chart::new(ChartType::AreaPercentStacked);
// Configure the first series.
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories("Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7")
.set_values("Sheet1!$B$2:$B$7")
.set_name("Sheet1!$B$1");
// Configure the second series.
chart
.add_series()
.set_categories("Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7")
.set_values("Sheet1!$C$2:$C$7")
.set_name("Sheet1!$C$1");
// Add a chart title and some axis labels.
chart.title().set_name("Percent Stacked Chart");
chart.x_axis().set_name("Test number");
chart.y_axis().set_name("Sample length (mm)");
// Set an Excel chart style.
chart.set_style(13);
// Add the chart to the worksheet.
worksheet.insert_chart_with_offset(33, 3, &chart, 25, 10)?;
workbook.save("chart_area.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}