Adding data to a worksheet
To add some sample expense data to a worksheet we could start with a simple program like the following:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}If we run this program we should get a spreadsheet that looks like this:
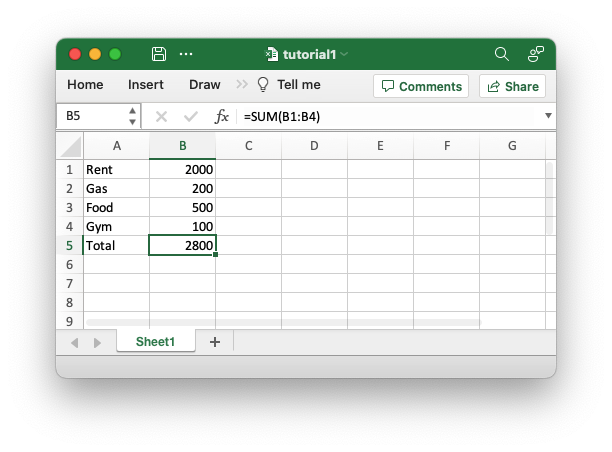
This is a simple program but it demonstrates some of the steps that would apply to any rust_xlsxwriter program.
The first step is to create a new workbook object using the
Workbook constructor Workbook::new():
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}Note, rust_xlsxwriter can only create new files. It cannot read or modify
existing files.
The workbook object is then used to add a new worksheet via the
add_worksheet() method:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}The worksheet will have a standard Excel name, in this case "Sheet1". You can
specify the worksheet name using the Worksheet::set_name() method.
We then iterate over the data and use the
Worksheet::write() method which converts common Rust
types to the equivalent Excel types and writes them to the specified row, col
location in the worksheet:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}Reading ahead:
There are other type specific write methods such as
Worksheet::write_string()andWorksheet::write_number(). However, these aren't generally required and thanks to Rust's monomorphization the performance of the genericwrite()method is just as fast.There are also worksheet methods for writing arrays of data or arrays of arrays of data that can be useful in cases where you don't need to add specific formatting:
Throughout rust_xlsxwriter rows and columns are zero indexed. So, for example,
the first cell in a worksheet, A1, is (0, 0).
To calculate the total of the items in the second column we add a
Formula like this:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}Finally, we save and close the Excel file via the Workbook::save() method
which will generate the spreadsheet shown in the image above.:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! A simple program to write some data to an Excel spreadsheet using
//! `rust_xlsxwriter`. Part 1 of a tutorial.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Formula, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Some sample data we want to write to a spreadsheet.
let expenses = vec![("Rent", 2000), ("Gas", 200), ("Food", 500), ("Gym", 100)];
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Iterate over the data and write it out row by row.
let mut row = 0;
for expense in &expenses {
worksheet.write(row, 0, expense.0)?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, expense.1)?;
row += 1;
}
// Write a total using a formula.
worksheet.write(row, 0, "Total")?;
worksheet.write(row, 1, Formula::new("=SUM(B1:B4)"))?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("tutorial1.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}Reading ahead:
The
Workbook::save()method takes astd::pathargument which can be aPath,PathBufor a filename string. It is also possible to save to a byte vector usingWorkbook::save_to_buffer().