Defined names: using user defined variable names in worksheets
Example of how to create defined names using the rust_xlsxwriter library.
This functionality is used to define user friendly variable names to represent a value, a single cell, or a range of cells in a workbook.
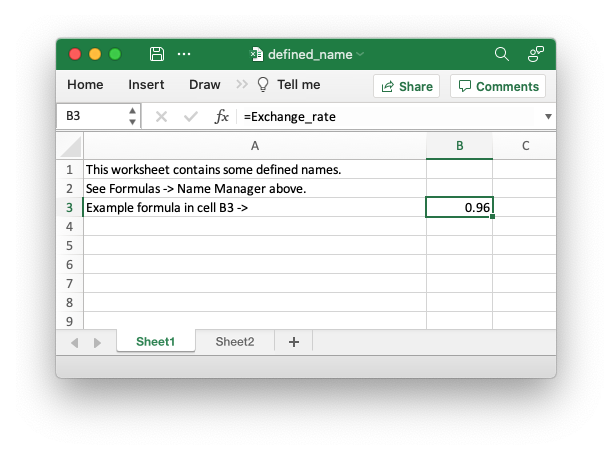
Images of the output file:
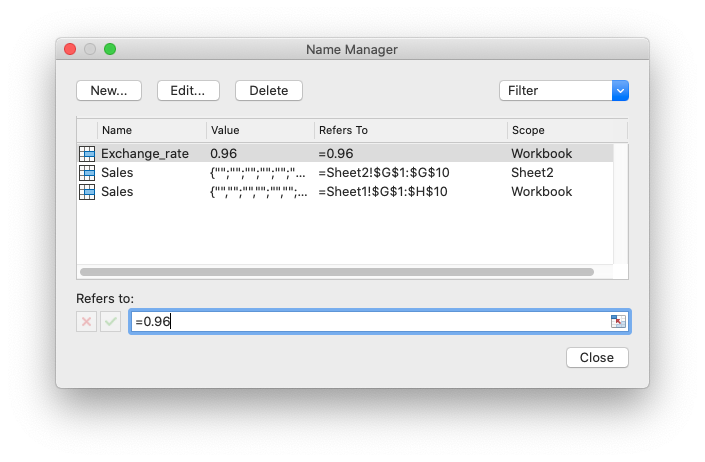
Here is the output in the Excel Name Manager. Note that there is a Global/Workbook "Sales" variable name and a Local/Worksheet version.
Code to generate the output file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! Example of how to create defined names using the `rust_xlsxwriter` library.
//!
//! This functionality is used to define user friendly variable names to
//! represent a value, a single cell, or a range of cells in a workbook.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add two worksheets to the workbook.
let _worksheet1 = workbook.add_worksheet();
let _worksheet2 = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Define some global/workbook names.
workbook.define_name("Exchange_rate", "=0.96")?;
workbook.define_name("Sales", "=Sheet1!$G$1:$H$10")?;
// Define a local/worksheet name. Over-rides the "Sales" name above.
workbook.define_name("Sheet2!Sales", "=Sheet2!$G$1:$G$10")?;
// Write some text in the file and one of the defined names in a formula.
for worksheet in workbook.worksheets_mut() {
worksheet.set_column_width(0, 45)?;
worksheet.write_string(0, 0, "This worksheet contains some defined names.")?;
worksheet.write_string(1, 0, "See Formulas -> Name Manager above.")?;
worksheet.write_string(2, 0, "Example formula in cell B3 ->")?;
worksheet.write_formula(2, 1, "=Exchange_rate")?;
}
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("defined_name.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}