Excel LAMBDA() function: Example of using the Excel 365 LAMBDA() function
An example of using the new Excel LAMBDA() function with therust_xlsxwriter
library.
See also The Excel 365 LAMBDA() function.
Image of the output file:
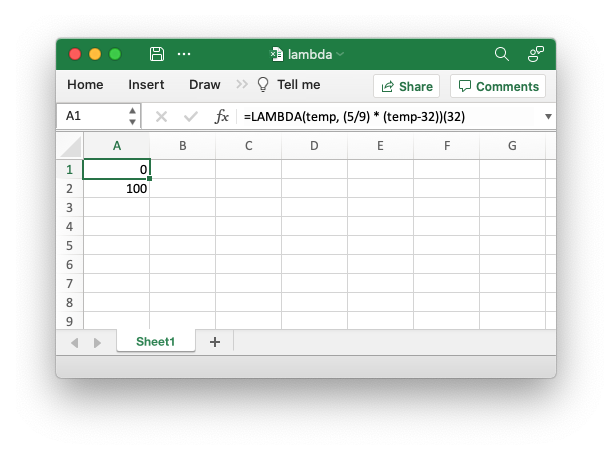
Code to generate the output file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! An example of using the new Excel LAMBDA() function with the `rust_xlsxwriter`
//! library.
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Write a Lambda function to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius to a cell as a
// defined name and use that to calculate a value.
//
// Note that the formula name is prefixed with "_xlfn." (this is normally
// converted automatically by write_formula*() but isn't for defined names)
// and note that the lambda function parameters are prefixed with "_xlpm.".
// These prefixes won't show up in Excel.
workbook.define_name(
"ToCelsius",
"=_xlfn.LAMBDA(_xlpm.temp, (5/9) * (_xlpm.temp-32))",
)?;
// Add a worksheet to the workbook.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Write the same Lambda function as a cell formula.
//
// Note that the lambda function parameters must be prefixed with "_xlpm.".
// These prefixes won't show up in Excel.
worksheet.write_formula(0, 0, "=LAMBDA(_xlpm.temp, (5/9) * (_xlpm.temp-32))(32)")?;
// The user defined name needs to be written explicitly as a dynamic array
// formula.
worksheet.write_dynamic_formula(1, 0, "=ToCelsius(212)")?;
// Save the file to disk.
workbook.save("lambda.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}