Chart: Gauge Chart
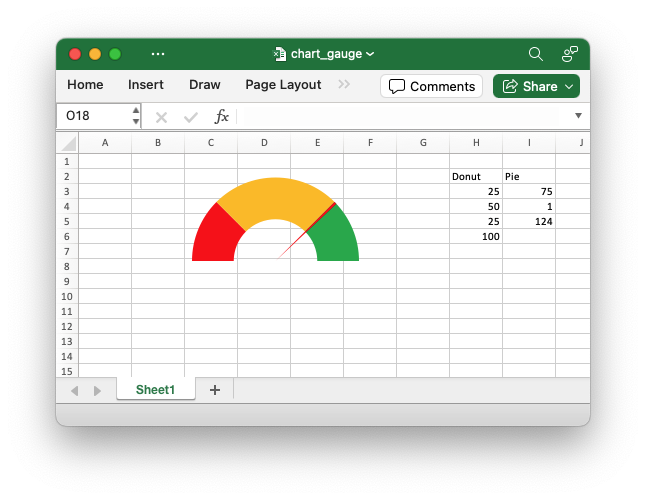
A Gauge Chart isn't a native chart type in Excel. It is constructed by combining a doughnut chart and a pie chart and by using some non-filled elements to hide parts of the default charts. This example follows the following online example of how to create a Gauge Chart in Excel.
Image of the output file:
Code to generate the output file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
//
// Copyright 2022-2026, John McNamara, jmcnamara@cpan.org
//! An example of creating a Gauge Chart in Excel using the `rust_xlsxwriter`
//! library.
//!
//! A Gauge Chart isn't a native chart type in Excel. It is constructed by
//! combining a doughnut chart and a pie chart and by using some non-filled
//! elements to hide parts of the default charts. This example follows the
//! following online example of how to create a [Gauge Chart] in Excel.
//!
//! [Gauge Chart]: https://www.excel-easy.com/examples/gauge-chart.html
//!
use rust_xlsxwriter::{
Chart, ChartFormat, ChartPoint, ChartSolidFill, ChartType, Workbook, XlsxError,
};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Add some data for the Doughnut and Pie charts. This is set up so the
// gauge goes from 0-100. It is initially set at 75%.
worksheet.write(1, 7, "Donut")?;
worksheet.write(1, 8, "Pie")?;
worksheet.write_column(2, 7, [25, 50, 25, 100])?;
worksheet.write_column(2, 8, [75, 1, 124])?;
// Configure the doughnut chart as the background for the gauge. We add some
// custom colors for the Red-Orange-Green of the dial and one non-filled segment.
let mut chart_doughnut = Chart::new(ChartType::Doughnut);
let points = vec![
ChartPoint::new().set_format(
ChartFormat::new().set_solid_fill(ChartSolidFill::new().set_color("#FF0000")),
),
ChartPoint::new().set_format(
ChartFormat::new().set_solid_fill(ChartSolidFill::new().set_color("#FFC000")),
),
ChartPoint::new().set_format(
ChartFormat::new().set_solid_fill(ChartSolidFill::new().set_color("#00B050")),
),
ChartPoint::new().set_format(ChartFormat::new().set_no_fill()),
];
// Add the chart series.
chart_doughnut
.add_series()
.set_values(("Sheet1", 2, 7, 5, 7))
.set_name(("Sheet1", 1, 7))
.set_points(&points);
// Turn off the chart legend.
chart_doughnut.legend().set_hidden();
// Rotate chart so the gauge parts are above the horizontal.
chart_doughnut.set_rotation(270);
// Turn off the chart fill and border.
chart_doughnut
.chart_area()
.set_format(ChartFormat::new().set_no_fill().set_no_border());
// Configure a pie chart as the needle for the gauge.
let mut chart_pie = Chart::new(ChartType::Pie);
let points = vec![
ChartPoint::new().set_format(ChartFormat::new().set_no_fill()),
ChartPoint::new().set_format(
ChartFormat::new().set_solid_fill(ChartSolidFill::new().set_color("#FF0000")),
),
ChartPoint::new().set_format(ChartFormat::new().set_no_fill()),
];
// Add the chart series.
chart_pie
.add_series()
.set_values(("Sheet1", 2, 8, 5, 8))
.set_name(("Sheet1", 1, 8))
.set_points(&points);
// Rotate the pie chart/needle to align with the doughnut/gauge.
chart_pie.set_rotation(270);
// Combine the pie and doughnut charts.
chart_doughnut.combine(&chart_pie);
// Insert the chart into the worksheet.
worksheet.insert_chart(0, 0, &chart_doughnut)?;
workbook.save("chart_gauge.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}